Media Contributed by Rick
Contributor
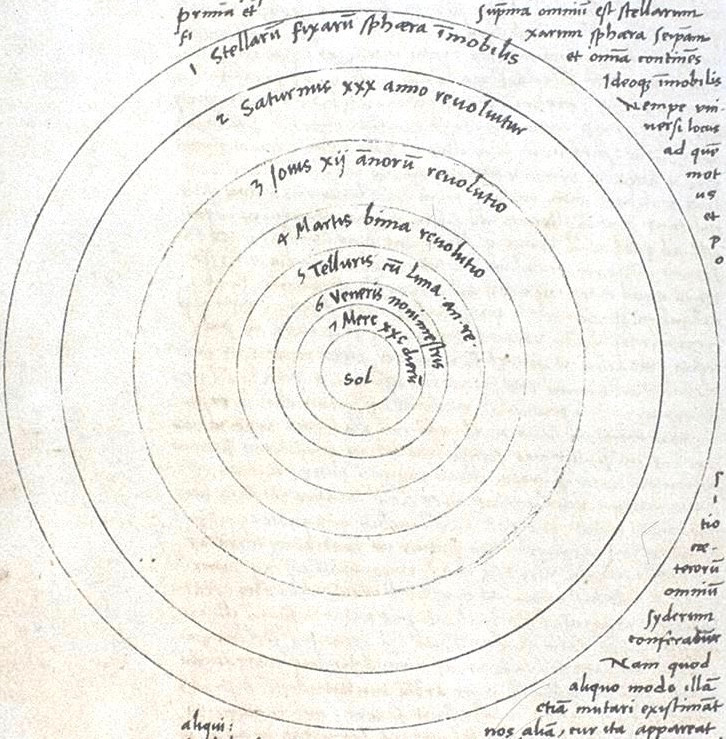
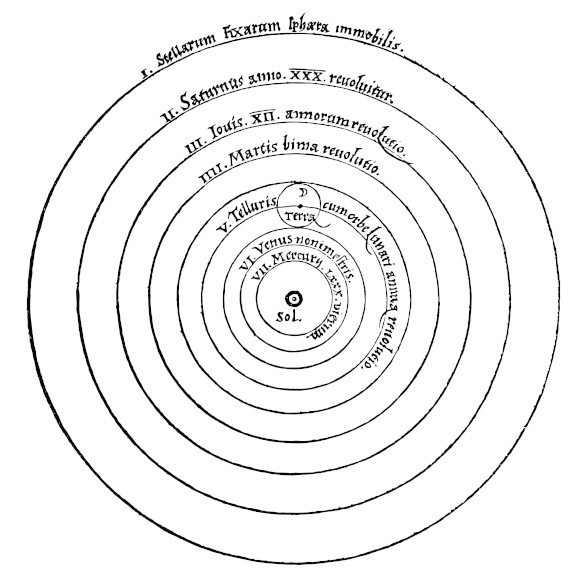
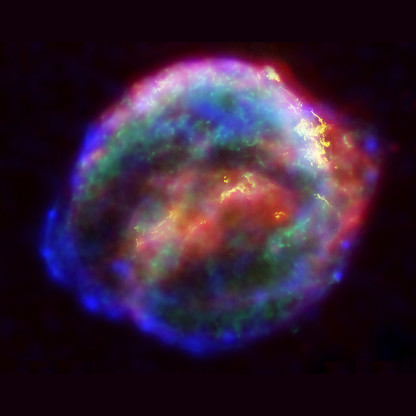



Not registered yet?
Register now! It is easy and done in 1 minute and gives you access to special discounts and much more!