Bavaria (Nation) AKA Bayern, Kingdom of Bavaria, Duchy of Bavaria

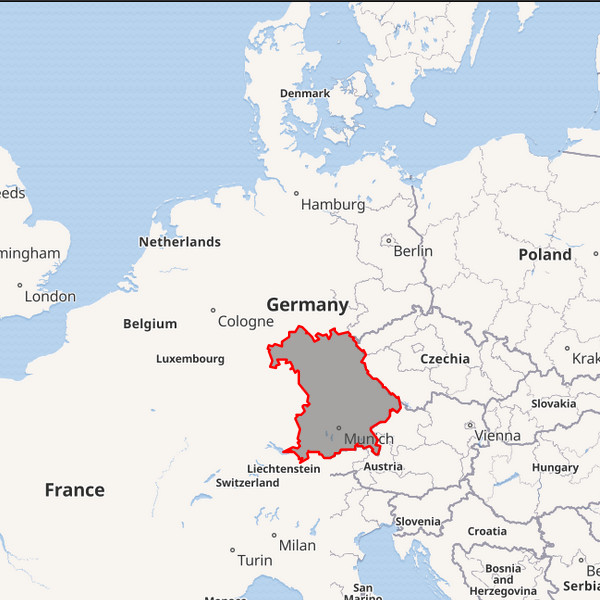
Bavaria
876 AD - 1918 AD
AKA Bayern, Kingdom of Bavaria, Duchy of Bavaria
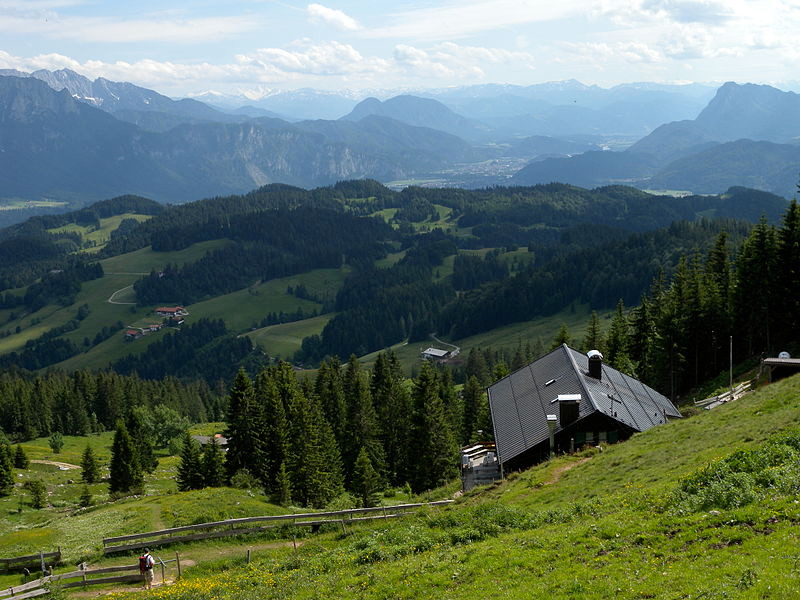
The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became a stem duchy in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an independent kingdom, joined the Prussian-led German Empire in 1871 while retaining its title of kingdom, and finally became a state of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.
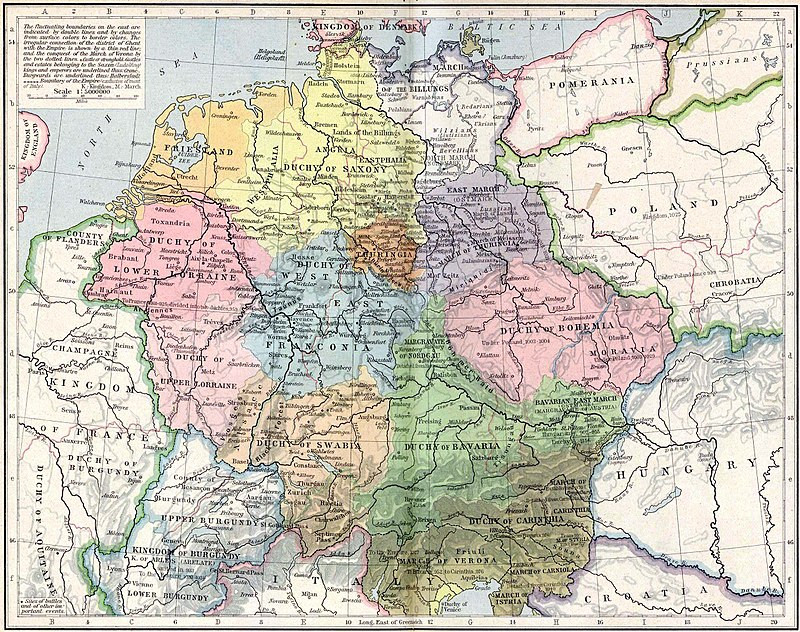
Duchy of Bavaria — A frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It dates back to the year 555 and was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes under Frankish overlordship. The capital was Regensburg until 1255 and later Munich from 1505.
Electorate of Bavaria — An independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
Kingdom of Bavaria — A German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918
Bavaria — officially the Free State of Bavaria is a landlocked state of Germany, occupying its southeastern corner. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometers (27,239.58 sq mi) Bavaria is the largest German state by land area comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany.
Events (16)
for 
Attachments
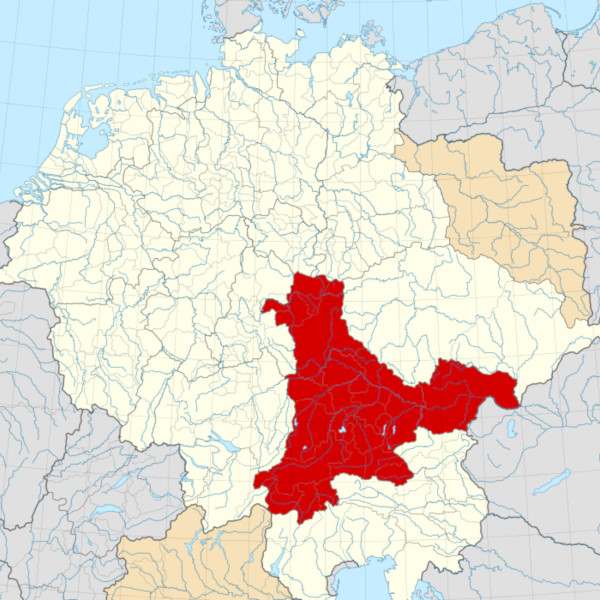
Duchy of Bavaria c.1000 CE Within the Holy Roman Empire, including the Austrian march
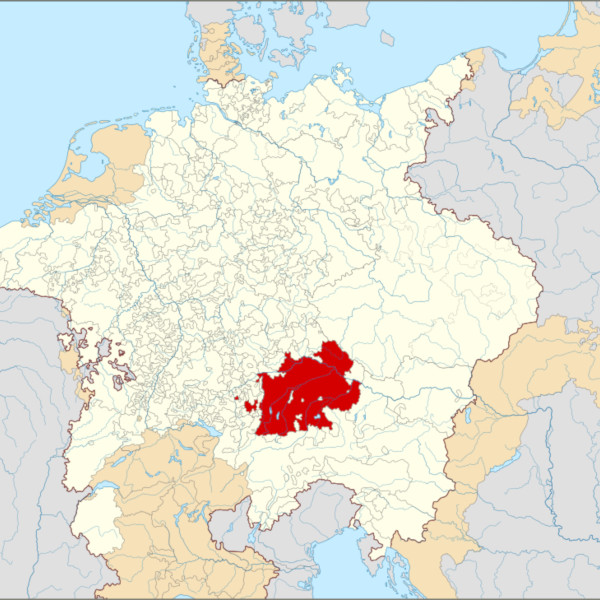
Duchy of Bavaria 1618 Within the Holy Roman Empire
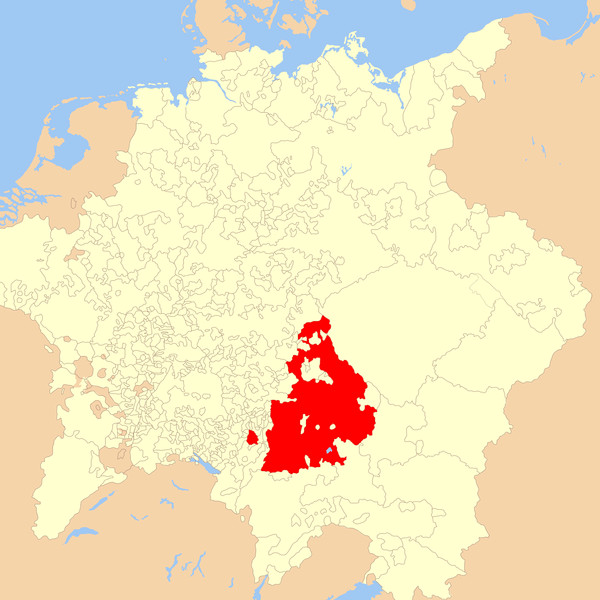
Electorate of Bavaria 1648 Within the Holy Roman Empire
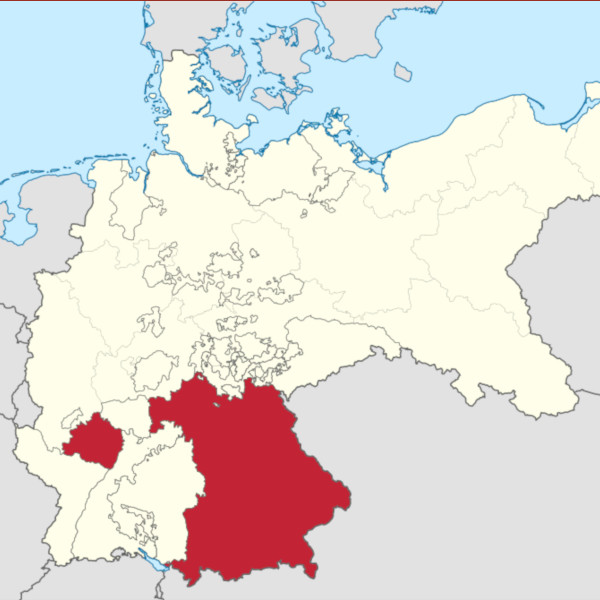
Kingdom of Bavaria Within the German Empire with the exclave of Palatinate
Free State of Bavaria Within the German Nation
Stem duchies of the German kingdom 919-1125 By William R. Shepherd (died 1934) - The Historical Atlas by William R. Shepherd, 1923.