Brown v. Board of Education - school segregation of races
05/17/1954 AD decided
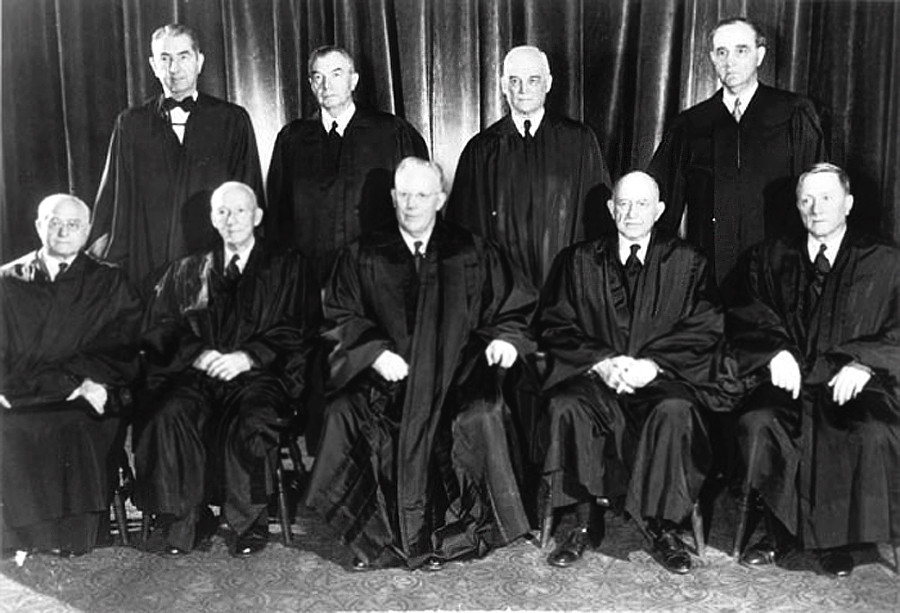
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segregated schools are otherwise equal in quality.
The Court's unanimous (9–0) decision stated that "separate educational facilities are inherently unequal", and therefore violate the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. However, the decision's 14 pages did not spell out any sort of method for ending racial segregation in schools, and the Court's second decision in Brown II only ordered states to desegregate "with all deliberate speed".
The case originated in 1951 when the public school district in Topeka, Kansas, refused to enroll the daughter of local black resident Oliver Brown at the school closest to their home, instead requiring her to ride a bus to a segregated black elementary school farther away. Unlike school districts of other states involved in the combined case, in Topeka the lower courts, while still requiring certain remedies, had found that the segregated schools were "substantially equal with respect to buildings, transportation, curricula, and educational qualifications of teachers." Hence with the involvement of the Kansas case the Supreme Court's findings specifically hinged upon the matter of segregation.
Lattitude: 38.9072° N
Longitude: 77.0369° W
Region: North America
Modern Day United States
Subjects Who or What decided?
-
Supreme Court of the United States The highest court in the...
Timelines (that include this event)
Events in 1954 MORE











