West Virginia splits from Virginia
10/24/1861 AD seceded from
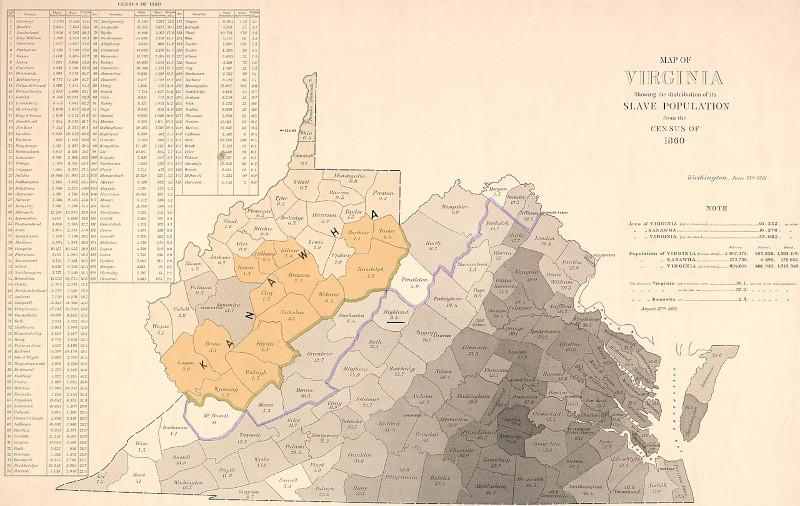
West Virginia was the only state in the Union to separate from a Confederate state (Virginia) during the Civil War. In Richmond on April 17, 1861, the Virginia Secession Convention of 1861 voted to secede from the Union, but of the 49 delegates from the northwestern corner (which ultimately became West Virginia) only 17 voted in favor of the Ordinance of Secession, while 30 voted against (with two abstentions).
Almost immediately after that vote, a mass meeting at Clarksburg recommended that each county in northwestern Virginia send delegates to a convention to meet in Wheeling on May 13, 1861. When this First Wheeling Convention met, 425 delegates from 25 counties were present, though more than one-third of the delegates were from the northern panhandle area. Soon there was a division of sentiment.
Some delegates led by John S. Carlile favored the immediate formation of a new state, while others led by Waitman Willey argued that, as Virginia's secession had not yet been passed by the required referendum (as happened on May 23), such action would constitute revolution against the United States.
The convention decided that if Virginians adopted the secession ordinance (of which there was little doubt), another convention including the members-elect of the legislature would meet in Wheeling in June 1861. On May 23, 1861, secession was ratified by a large majority in Virginia as a whole, but in the western counties 34,677 voted against and 19,121 voted for the ordinance.
The Second Wheeling Convention met as agreed on June 11 and declared that, since the Secession Convention had been called without popular consent, all its acts were void and all who adhered to it had vacated their offices.
The Wheeling Conventions, and the delegates themselves, were never actually elected by public ballot to act on behalf of western Virginia. Of its 103 members, 33 had been elected to the Virginia General Assembly on May 23. This included some hold-over state senators whose four-year terms had begun in 1859, and some who vacated their offices to convene in Wheeling. Other members "were chosen even more irregularly—some in mass meetings, others by county committee, and still others were seemingly self-appointed".
An act for the reorganization of the government was passed on June 19. The next day, convention delegates chose Francis H. Pierpont as governor of Virginia and elected other officers to a rival state government and two U.S. senators (Willey and Carlile) to replace secessionists before adjourning. The federal government promptly recognized the new government and seated the two new senators.
Thus there were two state governments in Virginia: one pledging allegiance to the United States and one to the Confederacy.
The second Wheeling Convention had recessed until August 6, then reassembled on August 20 and called for a popular vote on the formation of a new state and for a convention to frame a constitution if the vote were favorable. In the October 24, 1861, election, 18,408 votes were cast for the new state and 781 against.
The election results were questioned since the Union army then occupied the area and Union troops were stationed at many of the polls to prevent Confederate sympathizers from voting. This was also election day for local offices, and elections were also held in camps of Confederate soldiers, who elected rival state officials, such as Robert E. Cowan. Most pro-statehood votes came from 16 counties around the Northern panhandle.
Over 50,000 votes had been cast on the Ordinance of Secession, yet the vote on statehood garnered little more than 19,000.
Lattitude: 38.3472° N
Longitude: 81.6333° W
Region: North America
Modern Day United States
Subjects Who or What seceded from?
-
West Virginia (WV) Nation
Objects To Whom or What was seceded from?
-
Virginia (VA) State in the Mid-Atlanti...
Events in 1861 MORE